In the present era dominated by technological advancements and sustainability concerns, the recycling of used lithium-ion car batteries has become an imperative process.
As the world increasingly embraces eco-conscious choices, the focus on electric vehicles raises questions not only about their environmental friendliness but also about the recycling of essential components like batteries. This article delves into the realm of battery recycling technology and modern methods, shedding light on how to keep your electric city clean and sustainable.

The Significance of Lithium-ion Batteries in Electric Cars
Lithium-ion batteries stand as the backbone of modern electric vehicles, providing not only power but also playing a pivotal role in the vehicle’s performance and range. However, like any other power source, batteries have a lifecycle, and addressing the issue of handling them after they are no longer safe for use becomes increasingly crucial.
Structure and Lifecycle of Lithium-ion Batteries
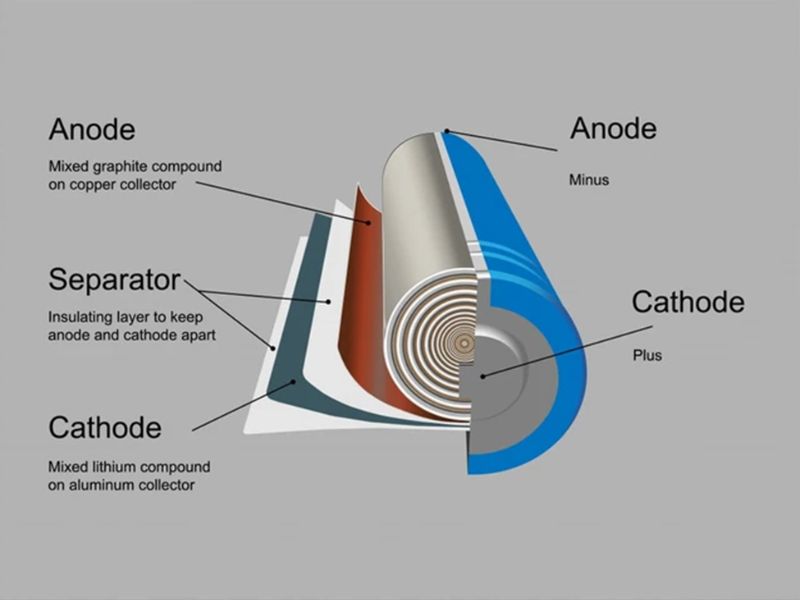
Before delving into the recycling process, it’s essential to understand the structure of lithium-ion batteries. The composition includes a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separator, and an electrolyte, all enclosed in an outer casing. These components contain vital materials such as lead, lithium oxide, and transition metals.
Modern Recycling Methods
Chemical Recycling: This method relies on the use of concentrated acid to separate the battery components. Used cells undergo treatment with various acids to create a metal ion solution, facilitating the convenient extraction of metals. Highly flexible, this method extracts up to 99% cobalt and lithium, along with 98% copper.
Thermal Recycling: Thermal recycling, or pyro-metallurgy, employs high temperatures to vaporize electrolyte and plastic in the battery. The melting process at the highest temperature aids in the recovery of cobalt, copper, and nickel, excluding lithium. While effective, this method is becoming less common due to its incompatibility with cobalt-free batteries.
Direct Physical Recycling: Direct physical recycling uses supercritical CO2 to separate the electrolyte. Subsequently, battery cells are fragmented, and physical metals like copper and aluminum are recovered. The remaining material forms the majority of the negative electrode and is heat-treated at high temperatures to enhance energy density and electrochemical performance.

The Importance of Lithium-ion Battery Recycling
Recycling lithium-ion batteries not only addresses the issue of waste management but also safeguards the Earth’s precious resources. If we aim to construct a sustainable electric vehicle future, battery recycling is not merely an option; it is a commitment to preserving our environment and resources.





* Your email address will not be published.